Commodity Futures Guide
1.About Commodity Futures
Commodity futures are derivative financial contracts that obligate the parties to sell or buy a certain commodity at a predetermined future date and price.
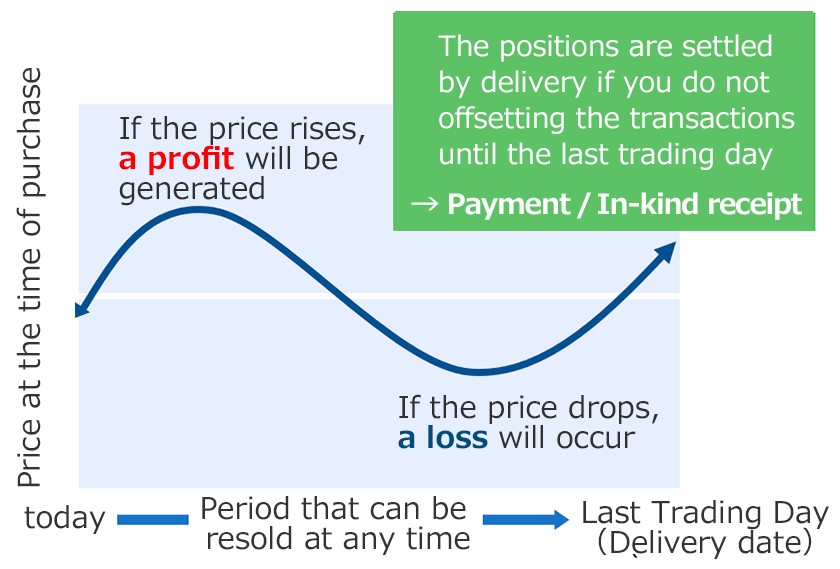
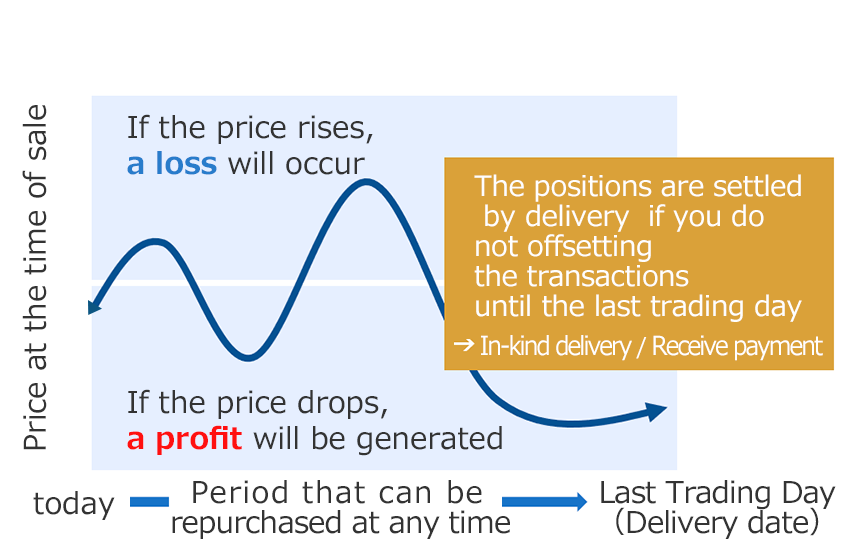
The buyer of a futures contract can sell their position at any time before last trading day and be free of their obligation. Traders can deal in price difference in the market and not through the actual transfer of commodities. The transfer of this difference is called as net settlement.
[Settlement of differences calculating formula] Futures profit or loss=(Selling price-Buying price)× magnification × Number of transactions
Therefore, it is possible to make a selling contract even if a seller does not have the commodities. It also makes it possible to make a buying contract without considering receiving the commodities. Since you can start trading from “sell” or “buy”, you would have the opportunity to make a profit regardless of whether the price is rising or falling, and this means it is useful as an asset management tool. For those who handle physical commodities such as producers, distributers and trading companies, it is also useful for conversion into cash and procurement of commodities by delivery settlement on the expiration date.
2.Underlying Assets of World’s Derivatives
Commodity derivative is one of the derivative transactions. Major underlying assets of world’s derivatives includes:
Until now, ODEX commodities market centered on agricultural commodity derivatives, but in the future, we will aim for the derivative market that targets various assets as described above.
| Commodity : Precious Metal | Gold,Silver,Platinum,Palladium |
|---|---|
| Commodity : Non-ferrous Metal | Copper,Aluminum,Zinc |
| Commodity : Energy | Crude oil,Gasoline,Natural gas |
| Commodity : Agricultural Crops | Corn,Soybeans,Wheat,Coffee beans |
| Currency | Dollar-Yen,Euro-Yen |
| Stock Index | Nikkei225,TOPIX,S&P500,Euro stoxx50 |
| Bonds・Interest Rate | JGB,US Treasury,Euribor |
3.Function
1)Asset Management
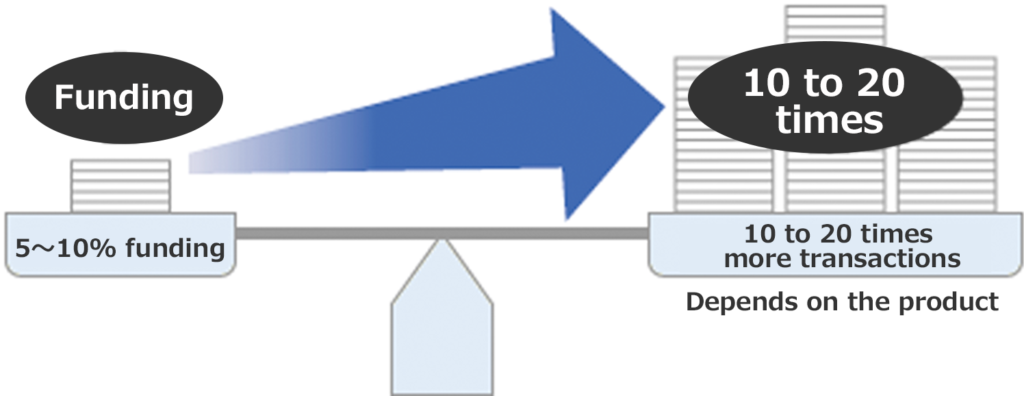
For example, if you participate in a transaction, you can deposit 50,000 yen (margin) as collateral, you can trade 10 to 20 times that amount 500,000 to 1 million yen. Many customers use this function as a tool of asset management because it is possible to close a transaction by settling the difference. In addition, it attracts attention as a part of the portfolio because it can be expected to have an efficient investment effect when it combined with other financial products.
2)Hedge
Those who are exposed to the risk of price fluctuations due to weather changes, exchange rate fluctuations, and supply and demand conditions can use the futures market as one of the tools to avoid these risks.
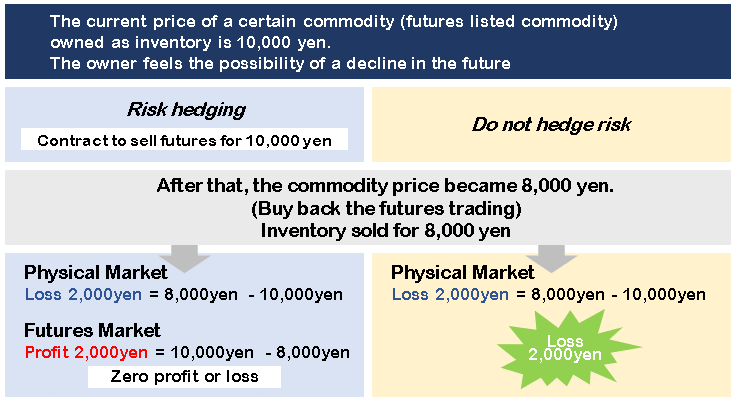
For example, when you anticipate future declines in the prices of listed commodities you hold in stock, you want to avoid the risk of price fluctuations until you can sell them. If you have a contract to sell futures at the current market price, you can expect to profit from futures and reduce losses even if the commodity price drops in the future.
If you anticipate that the market price will rise by the time you purchase products, you can make a contract to buy futures at the current market price, and you can purchase products at the contracted price even if the price increases in the future.
Hedge Transaction Example(Sell Hedge)
3)Price Formative Function
Futures trading has the function of forming prices by reflecting the ever-changing supply and demand. This function is called the price discovery function.
In the futures market, it is considered fairest because many sellers and buyers continuously present their orders (quantity and price) and determine the competitive price.
Therefore, the price is trusted by both the seller and the buyer, and is used as the standard and index price for physical transactions.
4.Margin
A feature common to all futures trading is that it is a “margin trading”. Margin is money or securities that a person holding an open contract in the futures market must pledge to a clearing organization as collateral for the execution of a transaction. A clearing organization is a corporation that is designated by a exchange and is responsible for the settlement of funds related to exchange transactions. Clearing margins for customers are also deposited to clearing organizations through commodity derivatives business operators.
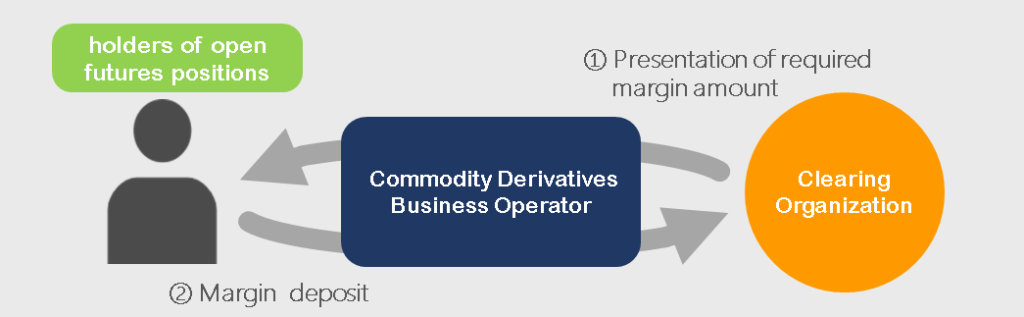
- Customers deposit margin through commodity derivatives business operator.
- The deposited margin will be used for liquidation such as “marking to market loss” and “settlement loss”.
5.Customer Protection System
About the System to Protect Customers’ Assets
Commodity derivatives business operators must ensure that the clearing margins they receive from customers are preserved. In preparation for unforeseen circumstances such as the bankruptcy of commodity derivatives business operators, the Commodity Derivatives Trading Act establishes the clearing margin system, the separated management system, and the entrustor protection fund system to protect customers’ assets.
a) Margin Protection
Under the clearing margin system, the margin deposited as collateral for transactions is obliged to be deposited to the Japan Securities Clearing Corporation (“JSCC”) directly by customers. Commodity derivatives business operators must deposit the clearing margin which is deposited by customers to JSCC. Customers normally request the refund of the deposited margin through commodity derivatives business operators, but if the commodity derivatives business operators cannot be refunded, such as when the commodity derivatives business operators goes bankrupt, the customer will directly request the refund to JSCC.
b) Separated Management System
Commodity derivatives business operators are obliged to segregate and manage the assets entrusted by customers to protect the customer’s claims (deposits to the JSCC, payment guarantees from banks, etc.). Therefore, even if commodity derivatives business operators go bankrupt, it can secure the resources to be used for payment of entrustment receivables.
c) Entrustor Protection Fund System
In the event that, for some reason, customer assets cannot be returned smoothly from bankrupt commodity derivatives business operators, the National Futures Protection Fund provides compensation of up to ¥10 million per customer for customer assets that cannot be returned.
